Understanding The Threats
Today’s modern identity-based email attacks exploit the identity of trusted colleagues and brands. However, each varies in the tactics and techniques used. Understanding the differences will be critical in being able to effectively and accurately stop these attacks.
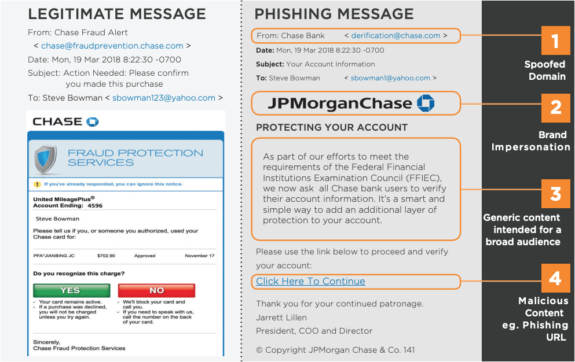
Customer Phishing: Cybercriminals use brand impersonation techniques such as domain spoofing and malicious content such as phishing URLs to evade security controls and trick their victims. Also, keeping content generic while launching scattershot attacks allows cybercriminals to reach as many recipients as possible.
Using Agari, we stopped 1.4 million potentially fraudulent emails from being delivered to customers per month.- Security Manager, Global 500 Financial Services Company
Business Email Compromise: BEC attacks differ from customer phishing by targeting employees of an organization. These targeted attacks inherently use identity deception, requiring no malicious content, such as phishing URLs or malware. BEC relies on three deception techniques: Display Name Imposter (DNI), Domain Spoofing, and Look-alike Domains. While all these routinely bypass Secure Email Gateways that by design look for malicious content, DNI-based attacks are the most effective.
Account Takeover (ATO)-Based Email Attacks: Cybercriminals use a multi-step process that initially compromises a previously established credible email account to launch subsequent targeted attacks such as BEC, spear phishing, or ransomware. ATO-based email attacks exploit the existing trust between the compromised account and its known contacts, which increases the cybercriminal’s success rate.

Fortra Advanced Email Security
Fortra Advanced Email Security is the most comprehensive email security architecture that detects, defends against, and deters advanced identity-based email attacks. With the Fortra Identity Graph at its core, the solution leverages a high-performance graph database of relationships and behavioral patterns between individuals, brands, businesses, services, and domains using hundreds of characteristics to maintain a real-time understanding of trusted communications to stop these attacks.